Understanding mTLS
Mutual Transport Layer Security (mTLS) is a robust security protocol that ensures two-way authentication and encryption between communicating parties. It’s an extension of the standard TLS protocol, which is widely used to secure internet traffic.
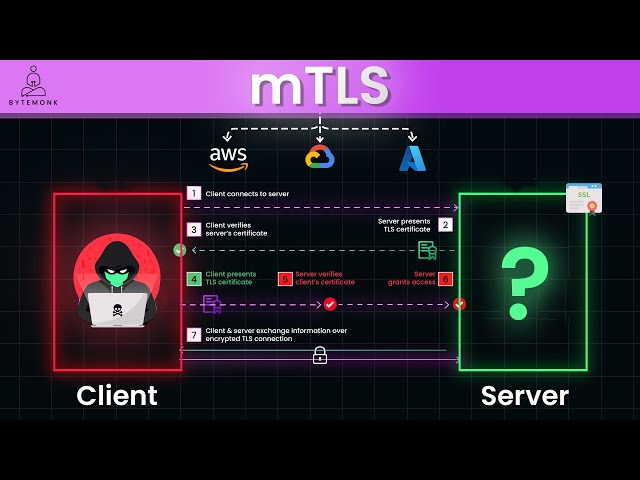
How mTLS Works
- Certificate Exchange: Both the client and the server possess digital certificates issued by a trusted Certificate Authority (CA).
- Authentication: The client and server exchange these certificates to verify each other’s identities.
- Session Key Generation: Once authentication is successful, they generate a shared secret key.
- Encrypted Communication: All subsequent communication is encrypted using this shared key, ensuring data confidentiality and integrity.
Benefits of mTLS
- Enhanced Security: By authenticating both parties, mTLS significantly reduces the risk of man-in-the-middle (MITM) attacks.
- Improved Data Privacy: Encrypted communication prevents unauthorized access to sensitive data.
- Simplified Security Architecture: mTLS can streamline security processes by eliminating the need for separate authentication mechanisms.
- Increased Trust: By verifying identities, mTLS fosters trust between the communicating parties.
Implementing mTLS in Microservices
- Obtain Certificates: Procure digital certificates from a trusted CA.
- Configure Servers: Configure your microservices to use mTLS. This typically involves specifying the certificate and private key.
- Client Configuration: Configure clients to trust the server’s certificate and present their own certificate.
- Secure Communication: Establish secure connections between microservices using mTLS.
Best Practices
- Strong Certificate Authority: Use a reputable CA to issue certificates.
- Regular Certificate Rotation: Rotate certificates periodically to minimize security risks.
- Secure Key Storage: Store private keys securely to prevent unauthorized access.
- Monitor and Log: Implement robust monitoring and logging to detect and respond to security incidents.
Leave a Reply